Rail Transport
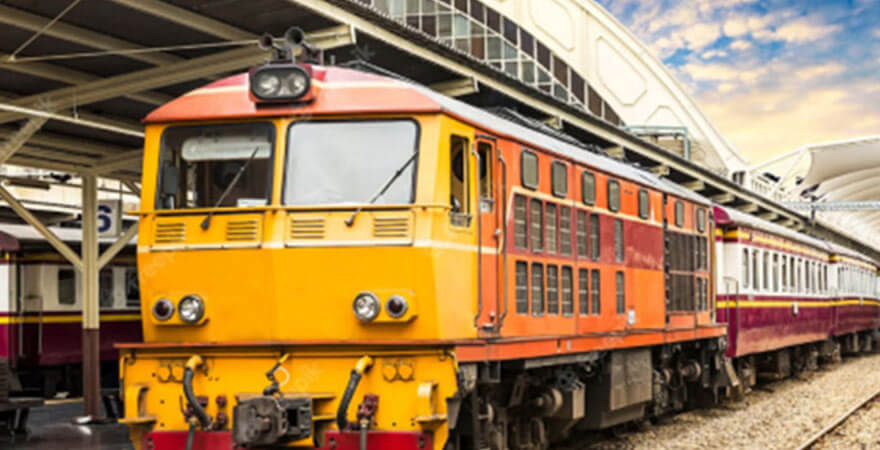

Rail Transport Services
Rail transport services form a critical component of the transportation infrastructure, offering a reliable and efficient mode of moving both passengers and freight. Rail networks are known for their sustainability, cost-effectiveness, and capacity to transport large volumes of goods over long distances, contributing to the economic development and connectivity of regions.
Key Features:
Efficient Mass Transportation:
Rail transport excels in efficiently moving large volumes of goods and passengers. The use of trains, with their capacity for numerous carriages, allows for economies of scale, making it a cost-effective solution for industries requiring mass transportation.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency:
Rail transport is recognized for its sustainability and energy efficiency. Electric and hybrid locomotives, as well as advancements in rail infrastructure, contribute to reduced carbon emissions and lower energy consumption compared to some other modes of transport.
Reliability and Punctuality:
Rail services are known for their reliability and punctuality. Fixed rail lines, well-maintained tracks, and controlled schedules contribute to on-time arrivals and departures, making rail a dependable option for both freight and passenger travel.
Cost-Effective for Long Distances:
For long-distance transportation, rail services are often more cost-effective than other modes. The ability to transport large quantities over extended distances in a single journey makes rail particularly suitable for industries such as logistics, manufacturing, and resource extraction.
Intermodal Connectivity:
Rail transport seamlessly integrates with other modes of transportation, creating an intermodal network. Intermodal hubs, where cargo can be transferred between trains, trucks, and ships, enhance the overall efficiency of the supply chain.
Challenges and Modernization:
Challenges in rail transport include infrastructure maintenance, capacity constraints, and competition from other modes. Ongoing efforts in modernization, such as the introduction of high-speed rail, digital signaling, and improved cargo handling technologies, address these challenges and enhance the overall effectiveness of rail services.
Technological Advancements:
Rail transport is undergoing technological advancements to improve safety, efficiency, and connectivity. Innovations include the implementation of digital signaling systems, automation in train control, and the development of high-speed rail networks to meet the demands of modern transportation.
Conclusion:
Rail transport services play a vital role in fostering economic development, sustainability, and connectivity. With ongoing advancements and a commitment to addressing challenges, rail transport remains a key contributor to the transportation landscape, providing efficient and environmentally friendly solutions for the movement of goods and people.